Fidget Spinner Mini-Project
Summary
I individually designed and generated the CNC tool paths for a fidget spinner toy. I then assembled a physical prototype.
Skills
CAD (SolidWorks); CAM (SolidWorks); Engineering drawings; Physical prototyping;
Team Size
1 (myself)
Category
Coursework: Design Tools II (AME 21268)
Detailed Breakdown
The goal of this project was to get hands-on experience with computer aided manufacturing (CAM). My professor provided me with 0.25” HDPE stock, a single 0.35” deep bearing, 1/4-20 hex nuts for weights, and plastic finger pads. Given these materials, I was tasked with designing and manufacturing a fidget spinner.
In the brainstorming phase of this project, I considered many tradeoffs regarding the behavior of the spinner including high rotational speed, long spin duration, and artistic ornamentation. I decided that it was important that my device be optimized for rotational speed. As such, my design was motivated by the idea of concentrating a large amount of mass very close to the center of rotation so as to create a relatively small mass moment of inertia.
I created my model based on this idea, with holes toleranced to accommodate the steel weighting nuts to be press-fit into them. I added additional circular holes near the outer edge of the fidget spinner to shift the weight distribution to be concentrated even nearer to the center hole.
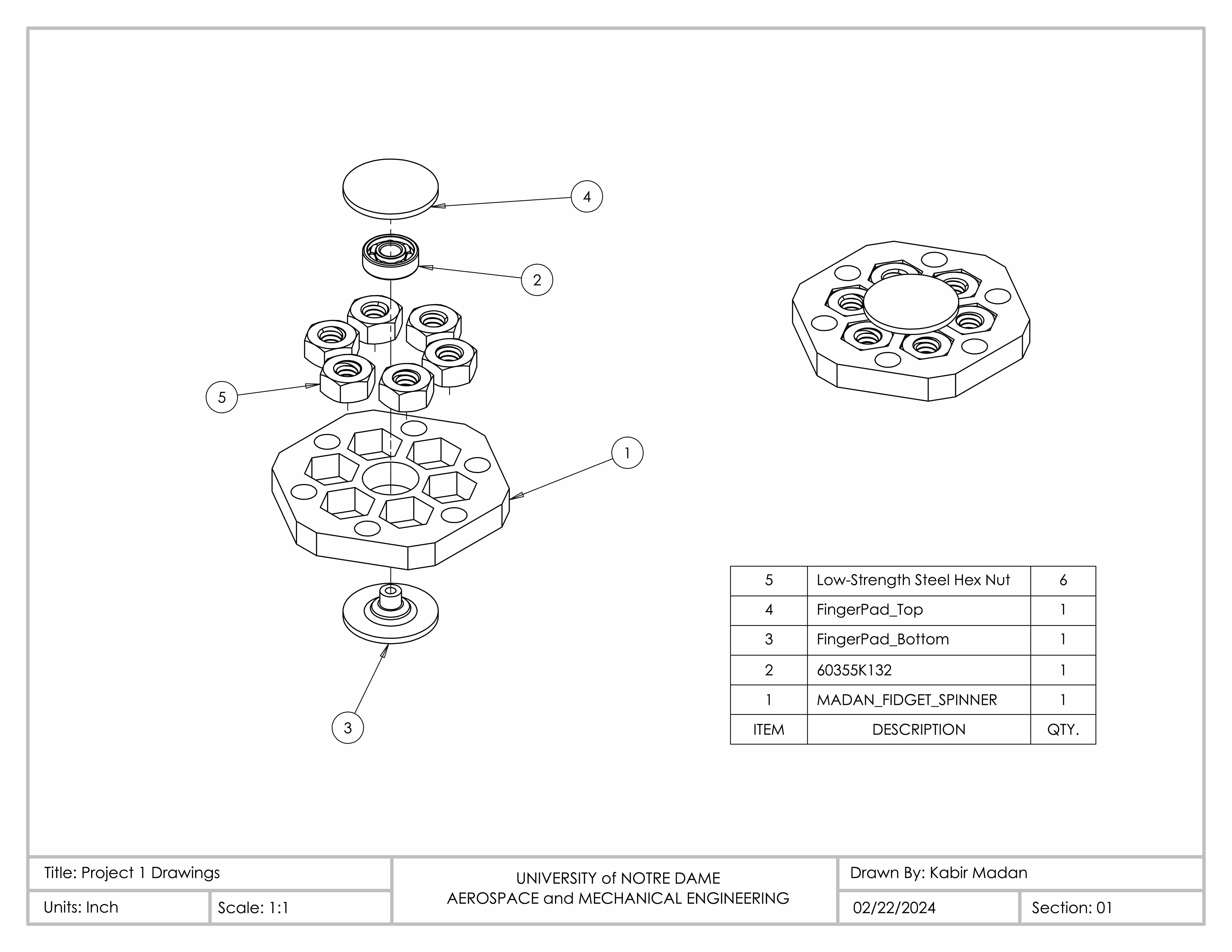
A drawing of the exploded view of the entire assembly.
Once I finalized the model, I specified the milling operations (just open pockets and a perimeter feature for this part) and generated the tool paths. I then generated the G-code and set the procedure to run on a Haas desktop mill. The final result is shown below.
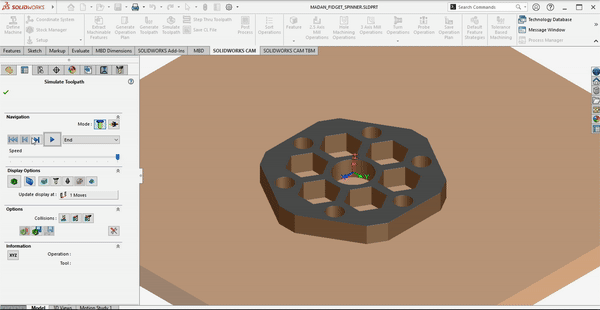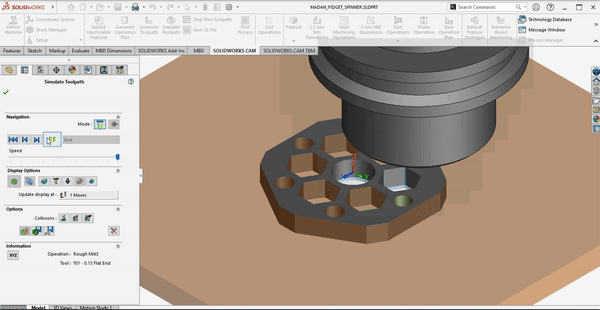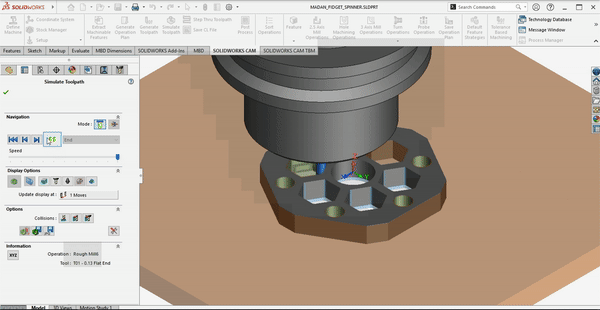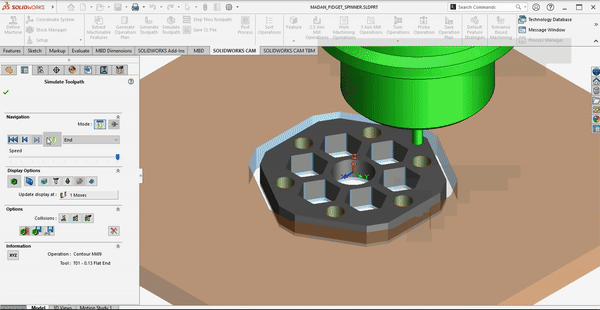
Tool path simulation.
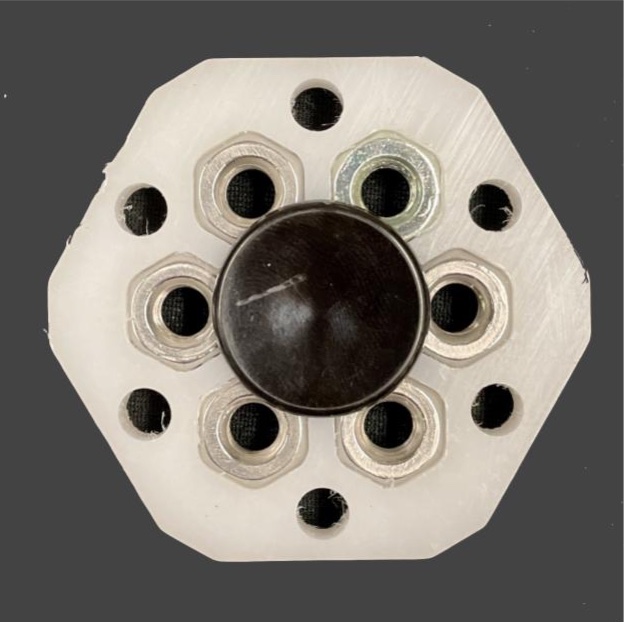

The result of the milled part with all components installed. Note that the outer holes were properly deburred after this photo was taken.